- OT
- CPD and education
- Medical retina
- Article
Medical retina
This VRICS feature considers the presentation, risk factors and causes of a series of medical retina conditions through fluorescein angiogram interpretation
Image A
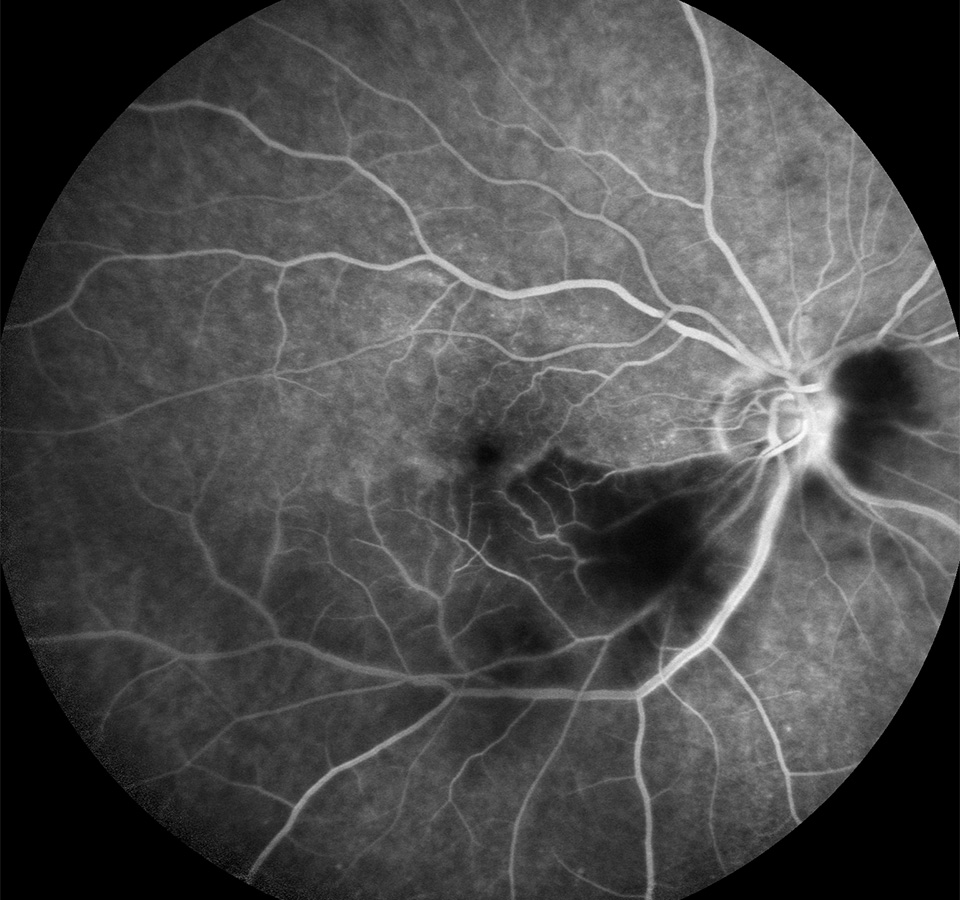
A 70-year-old man presents with symptoms of sudden onset.
01 Based on the fluorescein angiogram shown, which of the following symptoms is the patient likely to have?
a) Pain
b) Partial vision loss
c) Bilateral vision loss
d) Red eyes
02 Which of the following is not a risk factor for this condition?
a) Raised cholesterol
b) Hypotension
c) Atherosclerosis
d) Coronary artery disease
03 Which of the following is the most common cause of the above condition?
a) Carotid plaque emboli
b) Vasospasm secondary to migraine
c) Giant cell arteritis
d) Toxoplasmosis
Image B
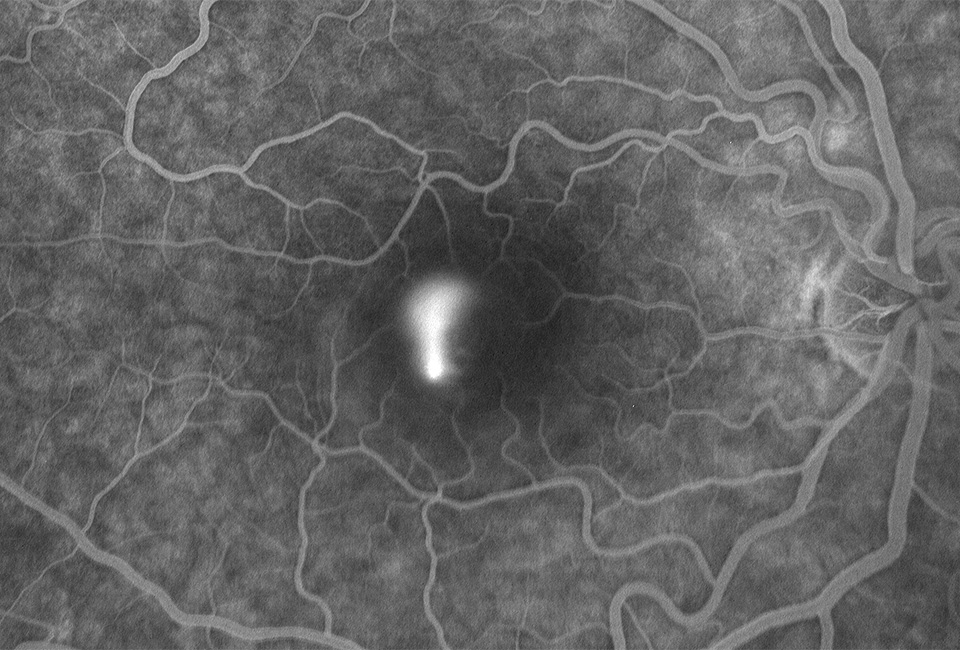
A 30-year-old businessman attends with blurred vision.
04 Which of the following statements about the condition above is false?
a) It typically affects men aged between 20-45 years age
b) It is more common in people of African descent
c) It is more common in those with a highly stressful occupation/lifestyle
d) Corticosteroid use can be a cause
05 Which of the following is the patient unlikely to present with?
a) Small myopic shift in prescription
b) Metamorphopsia
c) Abnormal colour vision
d) Reduced visual acuity
06 Which of the following would be a differential diagnosis?
a) Wet age-related macular degeneration
b) Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy
c) Optic nerve pit maculopathy
d) All of these options
Image C
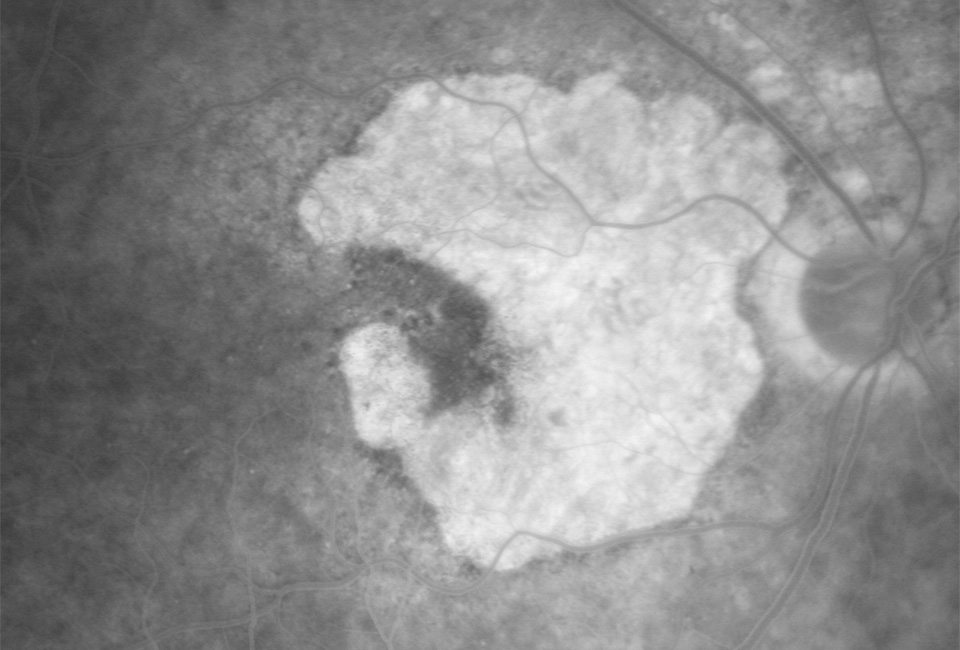
A 70-year-old woman presents with gradual vision loss.
07 Which of the following is not a risk factor for the above condition?
a) Increasing age
b) Positive family history
c) Current or previous smoking
d) African descent
08 Which of the following statements about ancillary testing is false?
a) Fundus autofluorescence shows atrophic areas as hyperautofluorescence
b) Fundus photo shows well circumscribed retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) atrophy with underlying choroidal vessels visible
c) Fluorescein angiography shows a sharply delineated window defect due to RPE atrophy
d) OCT shows thinning of the RPE/Bruch’s membrane complex and loss of photoreceptor layers
09 Which of the following would be a differential diagnosis?
a) Stargardt disease
b) Myopic macular degeneration
c) Adult onset vitelliform macular dystrophy
d) All of these options
Image D
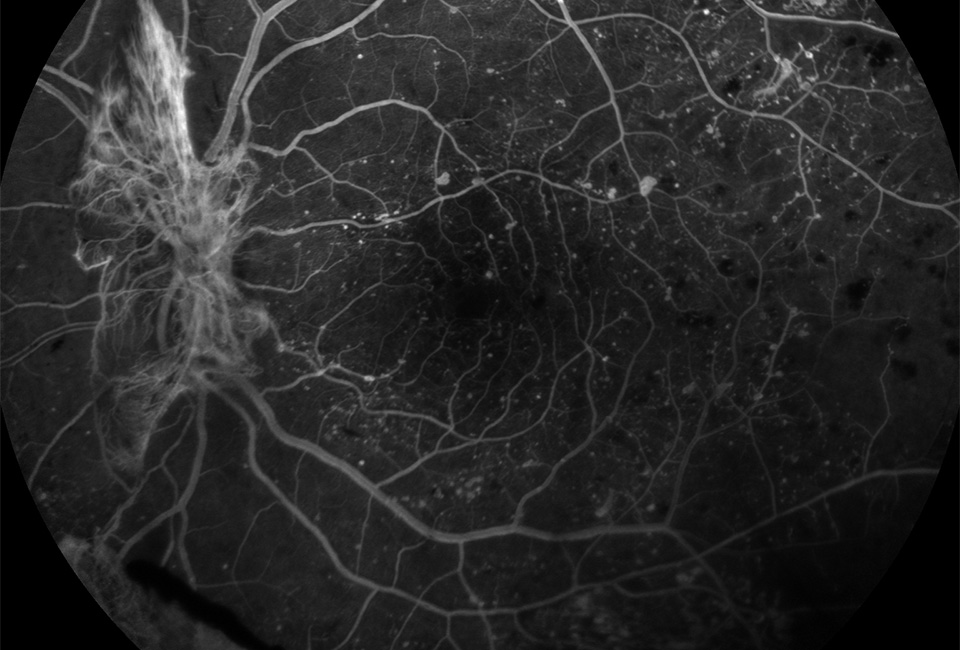
A 40-year-old patient from India presents with the signs shown in the image.
10 Considering the fluorescein angiogram above, which of the following signs is shown?
a) Hyperfluorescence at the optic nerve due to new disc vessels
b) Hypofluorescence at the optic nerve due to new disc vessels
c) Hyperfluorescence at the optic nerve due to intraretinal microvascular abnormalities
d) Hypofluorescence at the optic nerve due to vitreous haemorrhage
11 What other signs may be seen in patients with the presentation above?
a) New vessels elsewhere
b) Pre-retinal haemorrhage
c) Vitreous haemorrhage
d) All of these options
12 Which of the following statements about the treatment of this condition is false?
a) Pan retinal photocoagulation destroys hypoxic retina which reduces vascular endothelial growth factor production
b) Lucentis is usually the treatment of choice
c) Vitrectomy is used in cases of longstanding vitreous haemorrhage and tractional retinal detachment
d) Cryotherapy can be used in the presence of opaque media
About the authors
Prashant Shah MCOptom, PGDipOphth, DipClinOptom is an optometrist with postgraduate diplomas in ophthalmology and in clinical optometry and currently works in routine practice.
Yashita Shah MCOptom, PGDipOphth is an optometrist working in independent practice. She holds a postgraduate diploma in ophthalmology.
Advertisement
OT CPD See all View all OT CPD
-
Sleep disorders in the eye and related systemic disease
- CPD points: 1
- Closes: 01 Jul 2024
-
Dry eye disease and its impact on everyday wellbeing
- CPD points: 1
- Closes: 01 Jul 2024
-
Repeated low-level red-light therapy: the future of myopia management?
- CPD points: 1
- Closes: 01 Jul 2024
